Ex: http://www.counter-currents.com
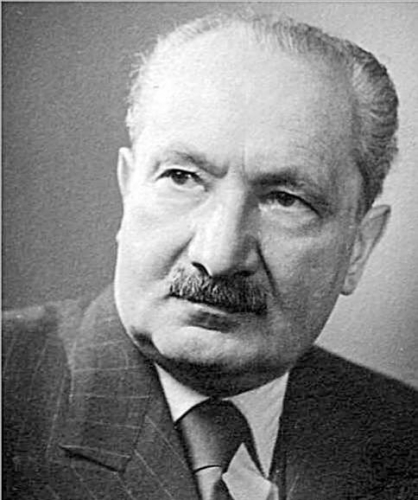
Thomas Rohkrämer
Martin Heidegger: Eine politische Biographie
Paderborn: Ferdinand Schöningh, 2020
“Heidegger passes the comeback test with the grade of fully satisfactory on both sides.”
— Carl Schmitt (1950) [1] [2]
“But what is essential is not counting but the right time — that is, the right moment and the right endurance. ‘For,’ as Hölderlin said, ‘the mindful god does detest untimely growth.'”
— Heidegger, An Introduction to Metaphysics
Céline once said: “Stalingrad. There’s the catharsis for you. The fall of Stalingrad was the end of Europe. There’s a cataclysm. The epicenter was Stalingrad. After that you can say white civilization was finished, really washed up.” [2] [3]
Was he right about that? Stalingrad, the decisive battle for the Germans, was a tragedy and cataclysm, no doubt, but was it really “the end of Europe”? This remark — and this question — have stuck with me since I encountered it here at Counter-Currents last year [4]. It speaks to a problem that I’m most familiar with from the work of Heidegger: Do we have a future?

At the end of the speech he gave when he assumed the rectorate of Freiburg University in May 1933, Heidegger foretells a future when “the spiritual force of the West fails, cracking in its joints, and its worn-out pseudo-culture collapses upon itself, dragging all forces into confusion and leaving them to suffocate in madness.” At this time, however, the cataclysm is not inevitable, for: “Whether such a thing happens or does not happen, that depends solely on whether we as a historical-spiritual Volk yet still again will ourselves — or whether we no longer will ourselves.” [3] [5] For Heidegger here, to truly “will” (or “want,” wollen, the German word is ambiguous) and assert “ourselves” is much more demanding than a thoughtless, vain, greedy insistence on the importance of one’s identity, power, or interests. For us to want and will ourselves, as a people, requires that we “know who we ourselves are,” and this knowing in turn can come only out of rigorous reflection on our Western historical Being — our heritage, our contemporary situation in its crisis, and our future possibilities — that is, it requires the guidance of a “thinking” of the peculiar sort that we now find at work in all of Heidegger’s writings. But, by the end of the war, in May 1945, it had long been clear that this extraordinarily noble effort at last-ditch resistance had failed.
Where then does that leave us, in Heidegger’s view? For a long time, on the basis of a slight acquaintance with his later work, I was of the opinion that, all-in-all, and despite the vague, dimly hopeful intimations of the future — such as his musings on a “homecoming race” (heimkehrenden Geschlecht) in his reading of poet Georg Trakl [4] [6] — Heidegger basically agreed with Céline: “we’re finished . . . really washed up!” But of late, other writings, such as Contributions to Philosophy (which contains the most focused and extensive reflection on what another, new, beginning or “inception” in our history would involve), along with entries in the recently published Black Notebooks from the late 1940s, make me reconsider this opinion. And now this new “political biography” by Thomas Rohkrämer provides much more support for a revision of our understanding of Heidegger’s postwar work. [5] [7]

I had in fact given up reading Heidegger biographies decades ago on account of their unbearable, indignant tone, the way they play up the most trivial details of Heidegger’s rectorship for the sake of scandal, and especially their utter obliviousness to what is truly at stake in his political engagement and thinking. The authors of these books almost invariably seem to see themselves as self-appointed officials on Heidegger’s denazification “cleansing committee” (Bereinigungsausschuss), reconvened a half-century later — and in continuous session ever since — to prosecute him for sins that went undetected and unpunished the first time around. But Rohkrämer’s book is altogether different and worthy of your attention if you have interest in Heidegger — and even if you don’t, for it might spark one. (Yes, unfortunately, the book is in German, but perhaps a favorable review at Counter-Currents will induce the publisher to put out a translation sooner rather than later.)
Rohkrämer’s account is dispassionate and sober, but yet utterly engaging at the same time, the latter by virtue of his keen sense for what the main issues are for Heidegger, as well as a talent for presenting them. He has clearly read — and, I now see, written [6] [8] — much about the men who were grouped together and designated members of the “Conservative Revolution in Germany” (Heidegger, Schmitt, Spengler, Ernst, and Friederich Georg Jünger, among others) on account of their common advocacy of nationalist, elitist, anti-liberal, and generally anti-modern metapolitical ideas in the 1920s and early 30s.
However serious and deep Rohkrämer’s interest in his subject, he maintains a cool, scholarly, objective distance from it by means, for example, of a most frequent use of the word angeblich (“would-be,” “supposed”), in expositing Heidegger’s opinions (as in, “the Germans are the would-be ‘shepherds of being’”).
While Rohkrämer is often critical of Heidegger’s ideas, his criticisms are not unduly obtrusive, for they come in the form of questions that illuminate the matter at hand, rather than serve the usual purpose of self-righteous posturing. For instance, in a discussion of Heidegger’s conception of the genuine work of art as something that opens and grounds a “world,” — with a Greek temple the prime example — Rohkrämer not only sees (as most readers do not) that art here is political in that it shapes the outlook of a community, he goes further and points out something absolutely crucial that Heidegger himself does not make explicit: that this community must be ethnically and culturally homogeneous. “A community founding work of art stands in tension with a pluralistic world. Can the ‘Greek paradigm’ again become alive for a multicultural nation, or is there not a clear affinity to a rigorously ordered community which is united in a communal belief?” [7] [9] And then, to elaborate the point, he considers Leni Riefenstahl’s Triumph of the Will and whether it is not the best contemporary analogue of the Greek temple for the way in which helps establish and unify a people.

Rohkrämer’s treatment of Heidegger on art is just one instance of many where he takes up a theme of Heidegger’s work that is not obviously “political” to many or most readers — religion, “authenticity,” the Greek “inception,” technology are others — and shows how Heidegger’s concern with it is bound up with his radical völkisch metapolitics. This suggests that genuine philosophic thinking itself, for Heidegger, grows out of, or simply is, at root, the highest expression of the care for “one’s own.” [8] [10]
But what I find most useful about this book is the attention paid to the question of the continuity of Heidegger’s ethnonationalist concerns after the war, which was our initial query here: do the peoples of the West have a future, in Heidegger’s view? Is his work still devoted to “another inception” in our history? And if so, how does he do this, after the war, under the oppressive conditions of the American occupation and the new German Bundesrepublik? And, further, if his focus on preparation for “another inception” is maintained throughout the post-war era, why is there the impression that he has given up serious efforts at the “salvation of the West” that he spoke of so movingly in 1937? [9] [11] This is a large constellation of questions, yes, but one might begin to orient oneself here by considering one question posed in a section title in chapter five, the most rewarding part of Rohkrämer’s book: “Continuity in Change: An Unsuccessful Denazification?” The following discussion is less a review of Rohkrämer’s excellent book, than my own rumination on these matters after an initial reading of the Black Notebooks and other texts from the years of occupation.
But first, what does it mean to speak of “völkisch metapolitics” — what is it that Heidegger is supposed to have “continued” or preserved after the war? For, admittedly, Heidegger never uses such a phrase to describe his own thinking or opinions — indeed he always resists, modifies, calls into question, or rejects altogether the use of such words in the meaning they carry in everyday “public” discourse. This holds true for concepts like “Volk,” “politics,” and “nationalism,” as it does for “being,” “world,” “truth,” “death,” “history,” “present,” “past,” “present,” and “future.” This state of affairs, the “uprootedness” or “fallenness” of all language from a stratum of “primordial” signification, is what makes the work of inquiry, understanding, and clarification both necessary and challenging. In any case, Heidegger articulates what we will call his “nationalist” preoccupations in this 1945 explanation of his motivations at the beginning of the preceding decade: “I then saw in the movement coming to power the possibility for an inner gathering and renewal of the Volk, and a way in which it could find its historical-Western determination.” [10] [12] Heidegger, as far as I can tell, never repudiates this “possibility” of German and Western renewal. However, from early on, he did indeed criticize and come to reject National Socialist public ideology and government policy as a way of actualizing this possibility. In other words, what we might call Heidegger’s ethononationalism is to be distinguished from “what is peddled about today as the philosophy of National Socialism” — although it might coincide with the “inner truth and greatness” of the latter that Heidegger affirmed in 1935 — and then reaffirmed in 1953. [11] [13)

You can buy Greg Johnson’s Graduate School with Heidegger here [15]
Heidegger’s criticism of National Socialism can be boiled down to two interrelated points. First, aside from whatever virtues they may have possessed, “these people,” i.e., the leaders of “the movement,” were “too naïve” in their thinking (as Heidegger said in his 1966 interview with the magazine Der Spiegel.) [12] [16] There was no one sufficiently “prepared” or “educated” to understand the depth of the problem posed by modern, technological nihilism, and what would constitute an adequate response. Second, despite its initial will to confront technological machination, National Socialism became manifest as just another form of the “will-to-power,” the metaphysics that governs the planet — then and now — and which was most adequately thought and described by Nietzsche and Ernst Jünger respectively. After an intense, decade-long confrontation with Nietzsche, [13] [17] Heidegger concluded that the very “desire to overcome” nihilism, [14] [18] metaphysics, and modernity has paradoxically led the Germans to become more inextricably entangled in its web.
And, aside from these criticisms, Heidegger came to see that it was an “error” on his own part to have not realized that the time for a new beginning had not yet arrived. “The error of 1933 consisted in the fact that it was not recognized how little prepared the forces were, and how little historically suitable.” [15] [19] But he still insists that the decision in 1933 was “essential” and not an error “in the world-historical sense” because the National Socialist regime was never considered to be an ultimate end or goal, but only a transition to something else, and thus an experience that one must first pass through in order to learn the lesson that must be learned. Whatever the error (or errors — Heidegger gives various descriptions of “der Irrtum 1933”), this self-reflection does not occasion regret, self-reproach — and certainly not guilt — but only further inquiry into the origins of the contemporary crisis, with a view to preparation for another commencement. Although this guiding intention remains throughout his life, from at least the late 1920s until his death in 1976, both the sense of what is possible, and the manner in which it can be communicated, changes at certain junctures, most notably in 1945, with the defeat, occupation, and “denazification” of Germany.
 Heidegger’s struggles under persecution during this era are of special interest for us today, given that we all now find ourselves subject to a new stage in what is basically the same process, what Stephen Paul Foster calls “Denazification, American Style [20].” Heidegger can help us confront this problem, for nobody has thought more deeply about this globalist-liberal attempt to irradicate the attachments to “one’s own” — family, Volk, race, community, land, heritage, customs, future — within the peoples of the West, and nobody has done more to prepare for a possible restoration of Western rootedness.
Heidegger’s struggles under persecution during this era are of special interest for us today, given that we all now find ourselves subject to a new stage in what is basically the same process, what Stephen Paul Foster calls “Denazification, American Style [20].” Heidegger can help us confront this problem, for nobody has thought more deeply about this globalist-liberal attempt to irradicate the attachments to “one’s own” — family, Volk, race, community, land, heritage, customs, future — within the peoples of the West, and nobody has done more to prepare for a possible restoration of Western rootedness.
Like most Germans who held official positions in the Third Reich, Heidegger was called before a “cleansing committee,” commissioned to investigate and punish supposed wrongdoings. He recognized that the real aim of the authorities here was to make the Germans feel and think themselves “guilty” in their very being for the suffering that humanity had experienced in the preceding half-century. Heidegger viewed the effect and significance of the occupation, and even the specific efforts to purge him and his work, in the deepest and broadest of terms. “However terrible to bear the destruction and devastation which have descended upon the Germans and their homeland may be, all that never reaches to the self-annihilation which now threatens our being [Dasein] in the betrayal of thinking.” [16] [21]
This process is to be understood as “self-annihilation” — and not simply the assault of foreign enemies — for a number of reasons. Heidegger’s own case was tried before his university senate, and so, as was typical with denazification tribunals, this was a case of “German against German.” [17] [22] And whereas earlier, in 1937, Heidegger saw Germany and Europe as threatened by the foreign, “the Asiatic” (whatever that means), now after the war it becomes clear that the Americans are most properly viewed as Europeans, and that the destruction of Europe — “the work of the Americans” — is in truth Europe’s “self-destruction.” [18] [23]
Moreover, as talk of German “guilt” and “disgrace” dominate public life, Heidegger reprises his early critique of the Christian-moral understanding of “guilt” and responsibility as a way in which Dasein evades and conceals from itself a fundamental awareness of its own groundlessness — i.e., that nothing and no one is ultimately responsible for the way things are. [19] [24] He now speculates on how the “artificially staged” discussion of guilt is a “façade” that conceals the true crisis faced by Germany and the West. [20] [25]
So at age 51 — the prime of life for a philosopher and teacher — Heidegger was expelled from university life: forced into retirement, denied a pension, forbidden to take part in university activities, and worst of all, from his own point of view, denied permission to teach students in any capacity. [21] [26] Considering the magnitude of the atrocities suffered under the Americans and Soviets, one might believe Heidegger fortunate.

But for Heidegger, this ordeal was experienced not so much as a personal affront and loss, but as the annihilation of the possibility of “thinking” itself, and that means the annihilation of the possibility of any future for Germany and the West. [22] [27] This sense of what is at stake here rests upon Heidegger’s own peculiar understanding of what “philosophy” or thinking “can and must be,” and that is (according to An Introduction to Metaphysics [1935]): “a thinking opening of the paths and vistas of the knowing that establishes measure and rank, in which and out of which a Volk conceives its Dasein in the historical-spiritual world and brings it to fulfillment — that knowing which ignites and threatens and necessitates all questioning and appraising.” [23] [28]
Along with Fichte, Shelling, and Hegel, Heidegger had considered the German university to be the “innermost determining center” of the Volk, the place where this national educational mission of philosophy is fulfilled. [24] [29] And he accordingly saw that this leadership role would be lost as authentic philosophy was replaced with “ersatz forms,” content to be the slave of “international moralism.” Newly vacant university positions could now be filled by the cultural Marxists who had left the country in the 1930s, and were now free to exact vengeance on Germany and the West, as Heidegger understood them. [25] [30]
For Heidegger, it was not only the Americans who failed to recognize that the destiny of the West depends entirely on the fate of authentic philosophic thinking. Under the “modern orders that have long prevailed” even the “nationalists of both young and old stamp” — and he here seems to include völkisch nationalists and radical conservatives — never acquired an adequate experience of “the world-wide historical determination of the Germans,” because they never seriously reflected on the questions such as: “who are we?” and “what is ‘our own?’” Heidegger now laments this “betrayal” because the Germans who have ascended to power under the victors are stridently hostile to any concern with the German heritage and destiny.
It is not that they have become indifferent and simply unreflective, rather they have adopted the mission of the enemy: “to pursue like a shadow and hinder every awakening into our own.” [26] [31] Under occupation and denazification, the Germans have made what is most “their own” into their enemy. Heidegger illustrates this now commonplace state of affairs with an odd quotation from an order which Winston Churchill, as Minister of the Navy in WWI, gave to British forces. He directed them to view “their own” vessels as possible enemies: “Be prepared to shadow possibly hostile men-of-war and consider H. M. ships under your command from this point of view.” [27] [32]

Heidegger believed that he was singled out for special persecution because of the danger that his thinking posed to the global liberal order. In a curious document (composed in 1946, but published posthumously in 2000), which presents itself as an unsent letter to an unnamed friend, Heidegger discloses — to us, readers of later generations — what he deliberately kept secret at the time. He writes, “Along with others, you wonder why my ‘denazification’ is still not finished. That can easily be explained. My being pushed to the side [Beseitigung] basically has nothing to do with Naziism. Rather, they sense something unsettling in my thinking, perhaps something uncanny, and they would like to get rid of it — that they at the same time take an interest in it, is only proof of this. . . . And as sharply as the Russians — i.e., European communistic technicism (which is not Russia) — oppose my thinking, just as clearly is it against the Anglo-American technocracy.” [28] [33] All contemporary ruling powers would thus discern a danger in Heidegger’s thought.
At the same time, he hints here that beyond or beneath and against the planetary technocracy there lies something like a “secret Russia” — just as he elsewhere suggests that there is a “secret Germany” and a “secret Evening-land” (i.e., the Occident or West), which has not been destroyed in the war, indeed has not yet emerged. [29] [34] In 1945, Heidegger writes, “Everyone now thinks about our downfall [Untergang]. But we Germans cannot go under, because we have not yet arisen and must first pass through the night.” [30] [35] The question we are left with then is: how do “we” make it through the night of the world, how do “we” prepare ourselves for a new morning?
The anonymous — most likely fictive — correspondent appears to have asked why the formal denazification process has not been terminated, as if to inquire, “why is your case taking so long?” But Heidegger’s response to the question seems to rely on a different sense of the word “unfinished.” With their reeducation efforts, the occupation authorities surely intended to elicit from the “guilty” ones a total repudiation and repentance of the thoughts, opinions, commitments, tastes, attitudes, and sentiments that they associate with what they call “Naziism.” If this is so, Heidegger’s “denazification” would never be “finished,” at least in the sense intended by these authorities.
And this seems to be the point Rohkrämer has in mind when he speaks of Heidegger’s “failed” or “unsuccessful” denazification. Rohkrämer provides much evidence of Heidegger’s resistance to the pressure exerted upon him to recant, “apologize,” admit his supposed “guilt” and alter the anti-liberal, anti-democratic, anti-American, nationalist direction of his thinking. Moreover, after the war, in 1945, precisely when the saving justice of American liberalism is supposed to have cleansed the world of the scourge of “German nihilism,” Heidegger writes that we now experience the full “completion of nihilism” and that the possible future recovery has already been announced in, and only in, “the poetic thinking and singing of the Germans.” [31] [36] Whereas in 1934 Heidegger had spoken of the “darkening of the world” (Weltdüsterung) to describe the historical moment, he now under American domination in 1946 suggests that “the world’s night is approaching its midpoint.” [32] [37] And unlike Celine’s Journey, this “night” may very well lead to morning (although it may require a few hundred years.)
So for Heidegger, the postwar period is truly a “needy time”: the philosopher who united thinking and teaching like no one before, and became the very greatest of teachers, found himself “deplatformed,” barred for the foreseeable future from lecture hall podium and the seminar. In this situation, there is no way Heidegger could openly educate those he calls “the ones to come” [33] [38] — die Zukünftigen — to enact a future “inception” and “homecoming” for Western man, and all of Heidegger’s postwar publications must be read with this in mind. Heidegger must now teach primarily through his writings, and these must, on the one hand, preserve and hold open essential possibilities for the “ones to come” who may live in the very distant future, and on the other hand, be sufficiently intelligible, interesting, and unoffensive to contemporaries that they are studied and preserved for that future.
Given the magnitude of these difficulties, the question as to how Heidegger carries out the task of saving the West in such an unpropitious time looms larger. In the note about his “unfinished” denazification, he claims, “I have been silent in thinking, not only since 1927, since the publication of Being and Time, but rather in this itself and constantly before.” [34] [39] Heidegger thus suggests that he always wrote for publication in a manner that somehow conveys what is essential, even as it preserves itself from both public distortion and persecution: by keeping silent.
This reference to meaningful silence may help explain, for example, why all explicit reference to das Volk — central even to the writings of the late 1930s — just disappears in the postwar publications (but not from the then-unpublished notebooks.) Heidegger obliquely calls attention to his deliberate silence about the Völkische in his response to an interview question about speeches he gave during his rectorate:
I would no longer write the lines you quote. Already in 1934 I would no longer have spoken them. But I would still today and even more decisively than before deliver the speech on the “Self-Assertion of the German University,” although without the reference to nationalism. Society has stepped into the place of the Volk. But in that respect the speech would today be spoken into the wind just as it was then. [35] [40]
Here we see how Heidegger adapts his discourse to altered historical circumstances, and that this adaptation requires consideration of what is politically appropriate and permissible to say, consideration of what is actual today (i.e., a liberal society of individuals in place of a Volk), and consideration of whether what one says will be heard and understood, or “spoken to the wind.” The circumstance that the Volk has been replaced by the liberal society of uprooted, historyless individuals would seem to render the possibility for an “inner gathering and renewal of the Volk” in the future especially problematic. [36] [43]

Rohkrämer helps us see how Heidegger and his compatriots on the political right modified their rhetoric in response to the difficulties posed by the oppressive post-war order. “One could no longer publicly express racism, but [other topics] — anticommunism, thoughts on the national community and the wishes for communal beliefs, the rejection of mass society, the call for an influential spiritual elite, cultural anti-Americanism, and the glorification of the Western tradition — could all very well be discussed.” [37] [44]
But here again, in this context, it is crucial to remind ourselves that throughout the post-war years, Heidegger never loses sight of the fundamental “errors” of National Socialism. I stress this point not as an “apologist” intent on preserving what remains of the academically respectable reputation of Heidegger (and the study of his works) from the presumed stain of fascism. Heidegger himself, and then also the public advocates managed or influenced by him, tried of course to put as much distance as possible between him and National Socialism. And we are grateful for their success: thanks to them, Heidegger’s stature as one of the greatest thinkers of the West has been established, his works are available everywhere, and many very helpful studies (including Rohkrämer’s) have been produced. The possibility of a new inception has thereby been handed down to us and future generations.
Nevertheless, we must recognize that this respectability has been built upon misunderstandings, or partial, superficial understandings, that make aspects of Heidegger’s thinking appealing to the liberal sensibilities of his contemporaries, but which distort or conceal his ethnonationalism. In any case, for us, the serious meaning of his twofold criticism of National Socialism — again, that leaders were unprepared in their thinking, and that the movement was too early because metaphysics had not yet reached its completion through planetary technocracy — is that it points to the necessity of making the hitherto inadequate or missing preparations for a new inception.
Taking only his most public statements into consideration, this task does not appear to be anything one would recognize as “political.” Consider, for example, Heidegger’s famous reply to a menial journalist, who asked if philosophy could do anything about the movement towards an “absolute technological state”: “Let me respond briefly and somewhat ponderously, but from long reflection: philosophy will not be able to effect an immediate transformation of the current condition of the world. This is not only true of philosophy, but of all merely human hitherto thought and endeavor. Only a god can save us. The sole possibility is to prepare a preparedness [eine Bereitschaft vorzubereiten] for the appearance of the god in thinking and poetry, or for the absence of the god in decline.” [38] [45]
 What is not made explicit here is that only “a god” can save “us” because only a communal orientation to a god — and not a scientific doctrine or a constitution — can meaningfully unify the German Volk. This völkisch-political dimension to Heidegger’s discourse on gods is however indicated elsewhere, in the difficult, enigmatic writings which were, by their author’s intention, withheld from publication until long after his death, for example, Contributions to Philosophy: “A Volk is only a Volk when it receives its history as apportioned in the finding of its god — that god which compels it to go beyond itself and thus to become a being.” [39] [46] And this political dimension is also at issue, if only obliquely, in Heidegger’s commentaries on Hölderlin, in which the gods require the building of a “house” within the “dwelling site” that must be founded. The poet’s “hymns” about a homecoming of the Germans, and a “founding” of a community united through a god, replaces secular political-metaphysical discourse — such as Hegel’s Philosophy of Right — as a way of thinking about national renewal. [40] [47]
What is not made explicit here is that only “a god” can save “us” because only a communal orientation to a god — and not a scientific doctrine or a constitution — can meaningfully unify the German Volk. This völkisch-political dimension to Heidegger’s discourse on gods is however indicated elsewhere, in the difficult, enigmatic writings which were, by their author’s intention, withheld from publication until long after his death, for example, Contributions to Philosophy: “A Volk is only a Volk when it receives its history as apportioned in the finding of its god — that god which compels it to go beyond itself and thus to become a being.” [39] [46] And this political dimension is also at issue, if only obliquely, in Heidegger’s commentaries on Hölderlin, in which the gods require the building of a “house” within the “dwelling site” that must be founded. The poet’s “hymns” about a homecoming of the Germans, and a “founding” of a community united through a god, replaces secular political-metaphysical discourse — such as Hegel’s Philosophy of Right — as a way of thinking about national renewal. [40] [47]
Thus Heidegger’s postwar focus on seemingly unpolitical topics — the essence of modernity, the problem of nihilism, technology, “poetic dwelling,” modern “homelessness,” language, and the origin and end of the history of the West — in fact serves the purpose of “preparation” for a new “inception,” a new form of ethnonationalist metapolitics in the future, at the right moment. In the conclusion of his book, Rohkrämer brilliantly describes this “continuity” of Heidegger’s concerns, and why they are subversive in a liberal, multicultural society:
Like most right-wing intellectuals, Heidegger deradicalized himself, and yet he remained anti-democratic and elitist, because he expected an awakening of the sense for the holy only from exceptional poets and thinkers. He remained focused on the Völkische, because for him the important things could emerge only out of one, above all his own German tradition, and not out of the effect of a pluralistic mixing and cross-pollination. Also, his conviction that only a god could save humanity points to the denial of plurality: in his vision of an ideal future, men are unified in a communal belief in one god. For being-with-one-another, or at least a harmonious coexistence in a world with different ideals in cultures and sub-cultures, Heidegger offers no answer. [41] [48]
According to Rohkrämer, then, Heidegger’s ideal future would presuppose ethnic, racial, and cultural homogeneity throughout the countries of the West, even as these are to be transformed and grounded anew through revolutionary, founding works of thinkers and poets. While that sounds right, it points to a further difficulty for us: what if the culture of “denazification” (i.e., “modernity”) brings ever more “pluralistic mixing,” such that “the holy heart of the peoples” (Hölderlin) — and thereby the West as a whole — dissolves into a multicultural dystopia?
Heidegger clearly saw that the trajectory of globalization was moving towards a world society and even a world government. [42] [49] And he clearly “hears,” and in his own way responds to, the “call to reflect on the essence of planetary domination” that he speaks of in his exchange with Ernst Jünger on nihilism. [43] [50] At the time that he writes this, in 1950, the peoples of Europe were still fairly homogeneous, and so it would not be surprising if many simply lacked awareness of the perils of encroaching pluralism. And in such a climate of moral opinion, no one, certainly not NSDAP members, was free to openly voice such concerns if he had them — as we today can surely appreciate. But given the depth of his preoccupation with the problem of a world society, and given the continuation of his völkisch concerns after the war, it is likely that Heidegger remains focused on the task of “preserving” and restoring the rootedness and integrity of the peoples of the West. [44] [51] And so we can now return to Heidegger’s postwar work and give it a much more careful reading, animated now by the hope that he can help us in our plight.
* * *
Counter-Currents has extended special privileges to those who donate $120 or more per year.
- First, donor comments will appear immediately instead of waiting in a moderation queue. (People who abuse this privilege will lose it.)
- Second, donors will have immediate access to all Counter-Currents posts. Non-donors will find that one post a day, five posts a week will be behind a “paywall” and will be available to the general public after 30 days.
To get full access to all content behind the paywall, sign up here:












 del.icio.us
del.icio.us
 Digg
Digg































 Le livre en question est une réflexion "métapolitique" sur la géopolitique, c'est-à-dire qu'il dépasse les questions spécifiques que traite cette discipline pour s'interroger sur le "pourquoi", sur les questions fondamentales dont découlent les questions géopolitiques et politiques tout court. Pourquoi s'occuper de géo-politique ? D'un point de vue immédiat, chaque État ne peut ignorer les questions géopolitiques, sous peine de graves conséquences. Un certain niveau de connaissances géopolitiques, c'est-à-dire des relations entre les États, est nécessaire à la classe politique de chaque État. Cependant, tous les États n'en ont pas besoin et ne peuvent pas l'utiliser de la même manière, cela dépend de la capacité d'action, qui dépend à son tour de la puissance d'un État. Un État qui est totalement subordonné aux politiques internationales d'un autre État, et il en existe, il faut le savoir, n'a guère besoin de connaissances géopolitiques puisque la décision sur les politiques internationales sera dictée par d'autres. Mais ce peu ne signifie pas zéro, un certain degré de connaissances géopolitiques est toujours nécessaire, une marge de manœuvre subsiste toujours, même si elle est devenue beaucoup plus étroite que la "souveraineté limitée" dont a bénéficié l'Italie de l'après-guerre jusqu'à l'effondrement de l'URSS. Mais si c'est le niveau immédiat d'où découle le besoin de connaissances géopolitiques, on ne peut s'y arrêter, sinon nous aurions une géopolitique purement nationaliste.
Le livre en question est une réflexion "métapolitique" sur la géopolitique, c'est-à-dire qu'il dépasse les questions spécifiques que traite cette discipline pour s'interroger sur le "pourquoi", sur les questions fondamentales dont découlent les questions géopolitiques et politiques tout court. Pourquoi s'occuper de géo-politique ? D'un point de vue immédiat, chaque État ne peut ignorer les questions géopolitiques, sous peine de graves conséquences. Un certain niveau de connaissances géopolitiques, c'est-à-dire des relations entre les États, est nécessaire à la classe politique de chaque État. Cependant, tous les États n'en ont pas besoin et ne peuvent pas l'utiliser de la même manière, cela dépend de la capacité d'action, qui dépend à son tour de la puissance d'un État. Un État qui est totalement subordonné aux politiques internationales d'un autre État, et il en existe, il faut le savoir, n'a guère besoin de connaissances géopolitiques puisque la décision sur les politiques internationales sera dictée par d'autres. Mais ce peu ne signifie pas zéro, un certain degré de connaissances géopolitiques est toujours nécessaire, une marge de manœuvre subsiste toujours, même si elle est devenue beaucoup plus étroite que la "souveraineté limitée" dont a bénéficié l'Italie de l'après-guerre jusqu'à l'effondrement de l'URSS. Mais si c'est le niveau immédiat d'où découle le besoin de connaissances géopolitiques, on ne peut s'y arrêter, sinon nous aurions une géopolitique purement nationaliste. 

















 Un héritage philosophique incandescent pour et contre
Un héritage philosophique incandescent pour et contre






 Dans les Principes du calcul infinitésimal, qui ont également été publiés en italien...
Dans les Principes du calcul infinitésimal, qui ont également été publiés en italien...


 Pourtant, les aspects métapolitiques du soi-disant "populisme" sont passés inaperçus en Italie...
Pourtant, les aspects métapolitiques du soi-disant "populisme" sont passés inaperçus en Italie...



 Avec Silvio Maresca nous réalisons tous deux, pour la télévision, un programme appelé "Disenso", qui porte sur la métapolitique et la philosophie, et cela depuis 2012 ; ce programme est accessible sur youtube. Et après avoir interviewé presque tous ceux qui essaient de faire de la philosophie en Argentine (s'il en reste, que nous aurions oubliés, nous les invitons à participer), nous avons commencé à traiter divers sujets philosophiques et ce commentaire en fait partie.
Avec Silvio Maresca nous réalisons tous deux, pour la télévision, un programme appelé "Disenso", qui porte sur la métapolitique et la philosophie, et cela depuis 2012 ; ce programme est accessible sur youtube. Et après avoir interviewé presque tous ceux qui essaient de faire de la philosophie en Argentine (s'il en reste, que nous aurions oubliés, nous les invitons à participer), nous avons commencé à traiter divers sujets philosophiques et ce commentaire en fait partie. Rien n'est plus éloigné de l'opinion de Heidegger, qui développe, à partir de là, la thèse centrale de la Lettre, selon laquelle la culture humaniste, en raison de sa rationalité moderne, celle de la raison calculatrice, ne pouvait nous apporter que la Seconde Guerre mondiale, avec sa civilisation de la technique à laquelle ont collaboré aussi bien le gigantisme nord-américain que le marxisme soviétique.
Rien n'est plus éloigné de l'opinion de Heidegger, qui développe, à partir de là, la thèse centrale de la Lettre, selon laquelle la culture humaniste, en raison de sa rationalité moderne, celle de la raison calculatrice, ne pouvait nous apporter que la Seconde Guerre mondiale, avec sa civilisation de la technique à laquelle ont collaboré aussi bien le gigantisme nord-américain que le marxisme soviétique. A quoi Heidegger répond brièvement en disant que l'éthique prédominante de la modernité a été l'éthique des normes, du devoir-être, qui se fonde sur l'éthique kantienne et la projection politique pratique de la morale bourgeoise, mais que tant l'éthique que l'ontologie sont des disciplines philosophiques établies depuis Platon, que les penseurs avant lui ne connaissaient pas en tant que telles.
A quoi Heidegger répond brièvement en disant que l'éthique prédominante de la modernité a été l'éthique des normes, du devoir-être, qui se fonde sur l'éthique kantienne et la projection politique pratique de la morale bourgeoise, mais que tant l'éthique que l'ontologie sont des disciplines philosophiques établies depuis Platon, que les penseurs avant lui ne connaissaient pas en tant que telles.








 Heidegger would have regarded Guénon and Evola as philosophically naïve—for several reasons. First, they uncritically appropriate the Western metaphysical tradition in the name of combating modernity. Yet, as I have already mentioned, Heidegger argues that that tradition is implicated in the decline of the West. Second, the Traditionalists naïvely assert that this metaphysical tradition is “perennial” or timeless. They take Platonism as preserving elements of a primordial tradition that antedates Plato by millennia. They hold that the time of Plato belongs to the Kali Yuga (the fourth age, the decadent “Iron Age”), but they take Plato (and other ancient philosophers) to be preserving an older, indeed timeless wisdom. However, this is pure speculation, for which there is no solid scholarly evidence.
Heidegger would have regarded Guénon and Evola as philosophically naïve—for several reasons. First, they uncritically appropriate the Western metaphysical tradition in the name of combating modernity. Yet, as I have already mentioned, Heidegger argues that that tradition is implicated in the decline of the West. Second, the Traditionalists naïvely assert that this metaphysical tradition is “perennial” or timeless. They take Platonism as preserving elements of a primordial tradition that antedates Plato by millennia. They hold that the time of Plato belongs to the Kali Yuga (the fourth age, the decadent “Iron Age”), but they take Plato (and other ancient philosophers) to be preserving an older, indeed timeless wisdom. However, this is pure speculation, for which there is no solid scholarly evidence. 





 Selon lui, la philosophie, pendant plus de 2000 ans d'histoire, a prêté attention à tout ce qui a les caractéristiques de l'"être" dans ce monde, y compris le monde lui-même, mais a oublié ce que cela signifie. C'est la "question de vie" de Heidegger, qui traverse toutes ses œuvres comme un fil rouge. Une des sources qui a influencé son interprétation de ce thème a été les travaux de Franz Brentano (photo) sur l'utilisation des différents concepts de l'être dans Aristote. Heidegger commence son œuvre principale, L’Etre et le Temps, par un dialogue tiré du Sophiste de Platon, qui montre que la philosophie occidentale a ignoré le concept d'être parce qu'elle considérait que sa signification allait de soi. Heidegger, pour sa part, exige que toute la philosophie occidentale retrace dès le début toutes les étapes de la formation de ce concept, appelant à un processus de "destruction" de l'histoire de la philosophie. Heidegger définit la structure de l'existence humaine dans son ensemble comme "Sorge" (= le Souci), qui est l'unité de trois moments : "être dans le monde", "courir en avant" et "être avec le monde de l'être". La "Sorge" est la base de "l'analyse existentielle" de Heidegger, comme il l'a appelée dans L'être et le temps. Heidegger pense que pour décrire une expérience, il faut d'abord trouver quelque chose pour laquelle une telle description a un sens. Ainsi, Heidegger déduit sa description de l'expérience à travers le Dasein, pour lequel l'être devient une question. Dans L’Etre et le Temps, Heidegger a critiqué la nature métaphysique abstraite des façons traditionnelles de décrire l'existence humaine, comme l’"animal rationnel", la personnalité, l'être humain, l'âme, l'esprit ou le sujet. Le Dasein ne devient pas la base d'une nouvelle "anthropologie philosophique", mais Heidegger le comprend comme une condition pour la possibilité de quelque chose comme "anthropologie philosophique". Selon Heidegger, le Dasein est "Sorge". Dans la partie sur l'analyse existentielle, Heidegger écrit que le Dasein, qui se trouve jeté au monde entre les choses et les Autres, trouve en lui la possibilité et l'inévitabilité de sa propre mort.
Selon lui, la philosophie, pendant plus de 2000 ans d'histoire, a prêté attention à tout ce qui a les caractéristiques de l'"être" dans ce monde, y compris le monde lui-même, mais a oublié ce que cela signifie. C'est la "question de vie" de Heidegger, qui traverse toutes ses œuvres comme un fil rouge. Une des sources qui a influencé son interprétation de ce thème a été les travaux de Franz Brentano (photo) sur l'utilisation des différents concepts de l'être dans Aristote. Heidegger commence son œuvre principale, L’Etre et le Temps, par un dialogue tiré du Sophiste de Platon, qui montre que la philosophie occidentale a ignoré le concept d'être parce qu'elle considérait que sa signification allait de soi. Heidegger, pour sa part, exige que toute la philosophie occidentale retrace dès le début toutes les étapes de la formation de ce concept, appelant à un processus de "destruction" de l'histoire de la philosophie. Heidegger définit la structure de l'existence humaine dans son ensemble comme "Sorge" (= le Souci), qui est l'unité de trois moments : "être dans le monde", "courir en avant" et "être avec le monde de l'être". La "Sorge" est la base de "l'analyse existentielle" de Heidegger, comme il l'a appelée dans L'être et le temps. Heidegger pense que pour décrire une expérience, il faut d'abord trouver quelque chose pour laquelle une telle description a un sens. Ainsi, Heidegger déduit sa description de l'expérience à travers le Dasein, pour lequel l'être devient une question. Dans L’Etre et le Temps, Heidegger a critiqué la nature métaphysique abstraite des façons traditionnelles de décrire l'existence humaine, comme l’"animal rationnel", la personnalité, l'être humain, l'âme, l'esprit ou le sujet. Le Dasein ne devient pas la base d'une nouvelle "anthropologie philosophique", mais Heidegger le comprend comme une condition pour la possibilité de quelque chose comme "anthropologie philosophique". Selon Heidegger, le Dasein est "Sorge". Dans la partie sur l'analyse existentielle, Heidegger écrit que le Dasein, qui se trouve jeté au monde entre les choses et les Autres, trouve en lui la possibilité et l'inévitabilité de sa propre mort.


 Le professeur Xiao Bin a souligné dans son livre "De l'État, du monde et de la nature humaine à la politique : la construction du concept politique de Schmitt", que l'homme lui-même est un être dangereux. "Il prétend que la politique est un danger pour les gens." La question suivante qui se pose lorsque l'on participe à la politique est d'expliquer ce qu'est la politique, en particulier la nature de la politique. La survie de l'unité nationale exige comme condition préalable une distinction entre ennemis et amis. Une politique fondée sur la séparation des ennemis et des amis est non seulement le destin inévitable de l'unité de la nation et de l'État, mais aussi la base de son existence. Schmitt a une compréhension unique de la nature de la politique : la norme de la politique est de séparer les amis et les ennemis. En fait, ce que nous appelons la politique implique la relation entre un ami et un autre, et la différence est l'intensité de cette différence. Cependant, nous ne pouvons pas ignorer le fait que les origines théologiques les plus secrètes et les plus mystérieuses et le nationalisme allemand ont un niveau de critères différent pour séparer les amis des ennemis.
Le professeur Xiao Bin a souligné dans son livre "De l'État, du monde et de la nature humaine à la politique : la construction du concept politique de Schmitt", que l'homme lui-même est un être dangereux. "Il prétend que la politique est un danger pour les gens." La question suivante qui se pose lorsque l'on participe à la politique est d'expliquer ce qu'est la politique, en particulier la nature de la politique. La survie de l'unité nationale exige comme condition préalable une distinction entre ennemis et amis. Une politique fondée sur la séparation des ennemis et des amis est non seulement le destin inévitable de l'unité de la nation et de l'État, mais aussi la base de son existence. Schmitt a une compréhension unique de la nature de la politique : la norme de la politique est de séparer les amis et les ennemis. En fait, ce que nous appelons la politique implique la relation entre un ami et un autre, et la différence est l'intensité de cette différence. Cependant, nous ne pouvons pas ignorer le fait que les origines théologiques les plus secrètes et les plus mystérieuses et le nationalisme allemand ont un niveau de critères différent pour séparer les amis des ennemis. Du point de vue ci-dessus, la politique émerge des conflits humains et les phénomènes politiques de la société humaine sont inévitablement associés aux conflits et à la coopération. Même si vous comprenez la politique en termes de bonté et de moralité, comme Aristote, elle ne peut pas cacher l'existence du mal. Sous le bien suprême se trouve la crise du mal. L'homme est l'existence de l'incertitude, l'homme est un animal politique naturel, et où qu'il soit, il y aura des conflits. Dans les conflits, il y aura inévitablement deux camps opposés et la politique ne peut pas se débarrasser du conflit... Les deux aspects du conflit et de la confrontation nous donnent une base logique pour la division en amis et ennemis.
Du point de vue ci-dessus, la politique émerge des conflits humains et les phénomènes politiques de la société humaine sont inévitablement associés aux conflits et à la coopération. Même si vous comprenez la politique en termes de bonté et de moralité, comme Aristote, elle ne peut pas cacher l'existence du mal. Sous le bien suprême se trouve la crise du mal. L'homme est l'existence de l'incertitude, l'homme est un animal politique naturel, et où qu'il soit, il y aura des conflits. Dans les conflits, il y aura inévitablement deux camps opposés et la politique ne peut pas se débarrasser du conflit... Les deux aspects du conflit et de la confrontation nous donnent une base logique pour la division en amis et ennemis.
 But Heidegger not only joined the Nazi party, he remained a member until it ceased to exist at the end of the Second World War. He attended conferences for Nazi
But Heidegger not only joined the Nazi party, he remained a member until it ceased to exist at the end of the Second World War. He attended conferences for Nazi  By contrast, Heidegger stressed that materialist satisfaction can never provide a truly meaningful existence. On the contrary, it can only produce tremendous anxiety as we recognize that the limitations of our lives and the inevitability of death will one day bring the party to an end. At that point, our pursuit of material satisfaction and wealth will turn out to have been meaningless. Heidegger argues that many of us realize this, and feel contempt for the vulgarity and emptiness of our societies. Nevertheless, rather than acknowledge this uncomfortable fact, we retreat into the inauthentic world of “das man” or the “they.” We try to ignore the inevitability of our annihilation by conforming to the expectations of consumer society, disregarding the deeper questions that drive us, and believing that, as long as we go about our business, death—and the confrontation with our own inauthenticity—can be postponed indefinitely.
By contrast, Heidegger stressed that materialist satisfaction can never provide a truly meaningful existence. On the contrary, it can only produce tremendous anxiety as we recognize that the limitations of our lives and the inevitability of death will one day bring the party to an end. At that point, our pursuit of material satisfaction and wealth will turn out to have been meaningless. Heidegger argues that many of us realize this, and feel contempt for the vulgarity and emptiness of our societies. Nevertheless, rather than acknowledge this uncomfortable fact, we retreat into the inauthentic world of “das man” or the “they.” We try to ignore the inevitability of our annihilation by conforming to the expectations of consumer society, disregarding the deeper questions that drive us, and believing that, as long as we go about our business, death—and the confrontation with our own inauthenticity—can be postponed indefinitely. Heidegger was one of the greatest philosophers in the twentieth century, despite his contemptible politics. There remains much we can learn from him, if we take care to isolate the gems of insight from the dangerous currents underneath. This is often a challenge whenever one is dealing with a critique of modernity that is powerful enough to be convincing. One must always take care not to trade the imperfect for the tyrannical.
Heidegger was one of the greatest philosophers in the twentieth century, despite his contemptible politics. There remains much we can learn from him, if we take care to isolate the gems of insight from the dangerous currents underneath. This is often a challenge whenever one is dealing with a critique of modernity that is powerful enough to be convincing. One must always take care not to trade the imperfect for the tyrannical.




 Ronald Beiner is a Canadian Jewish political theorist who teaches at the University of Toronto. I’ve been reading his work since the early 1990s, starting with What’s the Matter with Liberalism? (1992). I have always admired Beiner’s clear and lively writing and his ability to see straight through jargon and cant to hone in on the flaws of the positions he examines. He is also refreshingly free of Left-wing sectarianism and willing to engage with political theorists of the Right, like Leo Strauss, Eric Voegelin, Michael Oakeshott, and Hans-Georg Gadamer. Thus, although I was delighted that a theorist of his caliber had decided to write a book on the contemporary far Right, I was also worried that he might, after a typically open and searching engagement with our outlook, discover some fatal flaw.
Ronald Beiner is a Canadian Jewish political theorist who teaches at the University of Toronto. I’ve been reading his work since the early 1990s, starting with What’s the Matter with Liberalism? (1992). I have always admired Beiner’s clear and lively writing and his ability to see straight through jargon and cant to hone in on the flaws of the positions he examines. He is also refreshingly free of Left-wing sectarianism and willing to engage with political theorists of the Right, like Leo Strauss, Eric Voegelin, Michael Oakeshott, and Hans-Georg Gadamer. Thus, although I was delighted that a theorist of his caliber had decided to write a book on the contemporary far Right, I was also worried that he might, after a typically open and searching engagement with our outlook, discover some fatal flaw.

 Beiner doesn’t offer a very clear account of why Nietzsche thinks liberalism undermines human nobility. The short answer is that it is simply the political application of the slave revolt in morals, in which the aristocratic virtues of the ancients were transmuted into Christian and eventually liberal vices, and the vices of the enslaved and downtrodden were transmuted into virtues.
Beiner doesn’t offer a very clear account of why Nietzsche thinks liberalism undermines human nobility. The short answer is that it is simply the political application of the slave revolt in morals, in which the aristocratic virtues of the ancients were transmuted into Christian and eventually liberal vices, and the vices of the enslaved and downtrodden were transmuted into virtues.

 In Heidegger’s later terminology, Nietzsche and National Socialism were both “humanistic,” premised on the idea that the human mind creates culture, whereas in fact culture creates the human mind. No genuine belief can be chosen. It has to seize us. This is one of the senses of Heidegger’s later concept of Ereignis, often translated “the event of appropriation”: the beginning of a new historical epoch seizes and enthralls us. This is the meaning of Heidegger’s later claim that “Only a god can save us now” — as opposed to a philosopher-dictator.
In Heidegger’s later terminology, Nietzsche and National Socialism were both “humanistic,” premised on the idea that the human mind creates culture, whereas in fact culture creates the human mind. No genuine belief can be chosen. It has to seize us. This is one of the senses of Heidegger’s later concept of Ereignis, often translated “the event of appropriation”: the beginning of a new historical epoch seizes and enthralls us. This is the meaning of Heidegger’s later claim that “Only a god can save us now” — as opposed to a philosopher-dictator. Beiner is even more blatant in his advocacy of self-censorship in Heidegger’s case:
Beiner is even more blatant in his advocacy of self-censorship in Heidegger’s case:
 L’on parlera de réussites individuelles, ou de succès statistiques « d’apprenants » dans les examens généraux de fin d’études – mot absurde puisqu’il n ‘y aura pas eu de vrai commencement et de fondation assurée -, et de carrières, mais que vaut un savoir au sein d’une nation ou d’une nature de peuple fragilisée, et ignorant qu’elle porte en elle un destin, lequel la broiera si elle ne le maîtrise ? Cette question s’est posée au professeur Heidegger, le terme de professeur étant plus proche de la profession de foi que de l’exercice mécanique de répétitions vides, brillantes mais infécondes, comme une coque de noix vide.
L’on parlera de réussites individuelles, ou de succès statistiques « d’apprenants » dans les examens généraux de fin d’études – mot absurde puisqu’il n ‘y aura pas eu de vrai commencement et de fondation assurée -, et de carrières, mais que vaut un savoir au sein d’une nation ou d’une nature de peuple fragilisée, et ignorant qu’elle porte en elle un destin, lequel la broiera si elle ne le maîtrise ? Cette question s’est posée au professeur Heidegger, le terme de professeur étant plus proche de la profession de foi que de l’exercice mécanique de répétitions vides, brillantes mais infécondes, comme une coque de noix vide.


 Heidegger's thought came to prominence in the post-Soviet era through the work of a remarkable polyglot translator and charismatic philosopher, Vladimir Bibikhin (1938-2004). Not only did Bibikhin translate Being and Time into Russian, he also cultivated a generation of young philosophers through his widely-attended lectures at the University of Moscow. It is difficult to apply a label to Bibikhin's thought, and I shall not try to do so. Suffice it to say that Bibikhin attempted to graft Heidegger onto central currents in Russian thought in such a way as to renovate Russian culture in the post-Soviet era, not as a wholesale rejection of western thought but as an effort at correcting its sometimes baleful influence, especially in regard to the insensate selfishness and venality that made strong inroads into post-Soviet Russia under the guise of promoting a free market and capitalist democracy. Bibikhin fought against the hypocrisy of American democracy as reflected in Russia, the ostensibly principled pursuit of freedom concealing there, as elsewhere, naked greed and exploitation.
Heidegger's thought came to prominence in the post-Soviet era through the work of a remarkable polyglot translator and charismatic philosopher, Vladimir Bibikhin (1938-2004). Not only did Bibikhin translate Being and Time into Russian, he also cultivated a generation of young philosophers through his widely-attended lectures at the University of Moscow. It is difficult to apply a label to Bibikhin's thought, and I shall not try to do so. Suffice it to say that Bibikhin attempted to graft Heidegger onto central currents in Russian thought in such a way as to renovate Russian culture in the post-Soviet era, not as a wholesale rejection of western thought but as an effort at correcting its sometimes baleful influence, especially in regard to the insensate selfishness and venality that made strong inroads into post-Soviet Russia under the guise of promoting a free market and capitalist democracy. Bibikhin fought against the hypocrisy of American democracy as reflected in Russia, the ostensibly principled pursuit of freedom concealing there, as elsewhere, naked greed and exploitation.


 EUR 28,00
EUR 28,00


 Despite his claim that the cultural crisis brought on by worldwide technological advancement could not be solved by a wholesale adoption of Eastern traditions such as Zen Buddhism, Martin Heidegger engaged in many conversations with… Japanese scholars throughout his philosophical career. His first and perhaps most significant encounter with the East took place as early as 1919, eight years before the publication of Being and Time. After having attended Heidegger’s 1918 lectures, one of his Japanese students, Tomonobu Imamichi, introduced Heidegger to the concept of “being in the world.” In The Book of Tea (1906), Tomonobu’s teacher, Okakura Kakuzo had used these words to describe an aspect of Zhuangzi’s spiritual vision.
Despite his claim that the cultural crisis brought on by worldwide technological advancement could not be solved by a wholesale adoption of Eastern traditions such as Zen Buddhism, Martin Heidegger engaged in many conversations with… Japanese scholars throughout his philosophical career. His first and perhaps most significant encounter with the East took place as early as 1919, eight years before the publication of Being and Time. After having attended Heidegger’s 1918 lectures, one of his Japanese students, Tomonobu Imamichi, introduced Heidegger to the concept of “being in the world.” In The Book of Tea (1906), Tomonobu’s teacher, Okakura Kakuzo had used these words to describe an aspect of Zhuangzi’s spiritual vision. The Book of Tea uses the tea ceremony to explore the wabi-sabi aesthetic experience cultivated in Japanese Zen arts and crafts. The early German translation of The Book of Tea uses the words das-in-der-Welt-sein, which, via Imamichi, found their way into the heart and soul of Heidegger’s 1927 magnum opus. Interestingly, Heidegger’s philosophical career not only begins under Japanese influence, it also ends with it. One of the essays in his last work On the Way to Language is “A Dialogue on Language” between “a Japanese and an inquirer” who remain significantly unnamed…
The Book of Tea uses the tea ceremony to explore the wabi-sabi aesthetic experience cultivated in Japanese Zen arts and crafts. The early German translation of The Book of Tea uses the words das-in-der-Welt-sein, which, via Imamichi, found their way into the heart and soul of Heidegger’s 1927 magnum opus. Interestingly, Heidegger’s philosophical career not only begins under Japanese influence, it also ends with it. One of the essays in his last work On the Way to Language is “A Dialogue on Language” between “a Japanese and an inquirer” who remain significantly unnamed… …The thinkers of the Kyoto School of Philosophy were in favor of the war and have been collectively referred to as the “philosophers of nothingness”. Some of them had a constructive vision of how the Buddhist understanding of the void could complement the techno-scientific thinking of the West in order to bring about a new global civilization. Key figures among them, such as Nishida Kitaro, were students of Heidegger as early as the 1920s, and like Heidegger they saw the world war as the means to bring about a global culture that would ground techno-scientific development in a spirituality transcending insular and traditional values.
…The thinkers of the Kyoto School of Philosophy were in favor of the war and have been collectively referred to as the “philosophers of nothingness”. Some of them had a constructive vision of how the Buddhist understanding of the void could complement the techno-scientific thinking of the West in order to bring about a new global civilization. Key figures among them, such as Nishida Kitaro, were students of Heidegger as early as the 1920s, and like Heidegger they saw the world war as the means to bring about a global culture that would ground techno-scientific development in a spirituality transcending insular and traditional values.


 Dostoevsky asks us to suppose that we were able to arrive at a formulation of the laws of nature, including biological and psychological laws, so precise that we could calculate, in every case, what a man will do by knowing what is at that moment to his advantage – not as an individual – but as an organism that microcosmically expresses the survivalist egoism of Nature. A man who became aware of this calculation would spitefully do something else, anything else, just to prove that he was not “a piano key” or an “organ pedal” whose thoughts and passions could in principle be encompassed by a formula, tabulated, and predicted according to statistical probability. Dostoevsky equates the sum total of any comprehensive formula for the laws of nature, of the kind that physicists today are still searching for under the rubric of a theory of everything, with “an endlessly recurring zero” because it nullifies meaningful action.
Dostoevsky asks us to suppose that we were able to arrive at a formulation of the laws of nature, including biological and psychological laws, so precise that we could calculate, in every case, what a man will do by knowing what is at that moment to his advantage – not as an individual – but as an organism that microcosmically expresses the survivalist egoism of Nature. A man who became aware of this calculation would spitefully do something else, anything else, just to prove that he was not “a piano key” or an “organ pedal” whose thoughts and passions could in principle be encompassed by a formula, tabulated, and predicted according to statistical probability. Dostoevsky equates the sum total of any comprehensive formula for the laws of nature, of the kind that physicists today are still searching for under the rubric of a theory of everything, with “an endlessly recurring zero” because it nullifies meaningful action.
